IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Disclaimer
Hip joint replacement is intended for use in individuals with joint disease resulting from degenerative and rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, fracture of the neck of the femur or functional deformity of the hip.
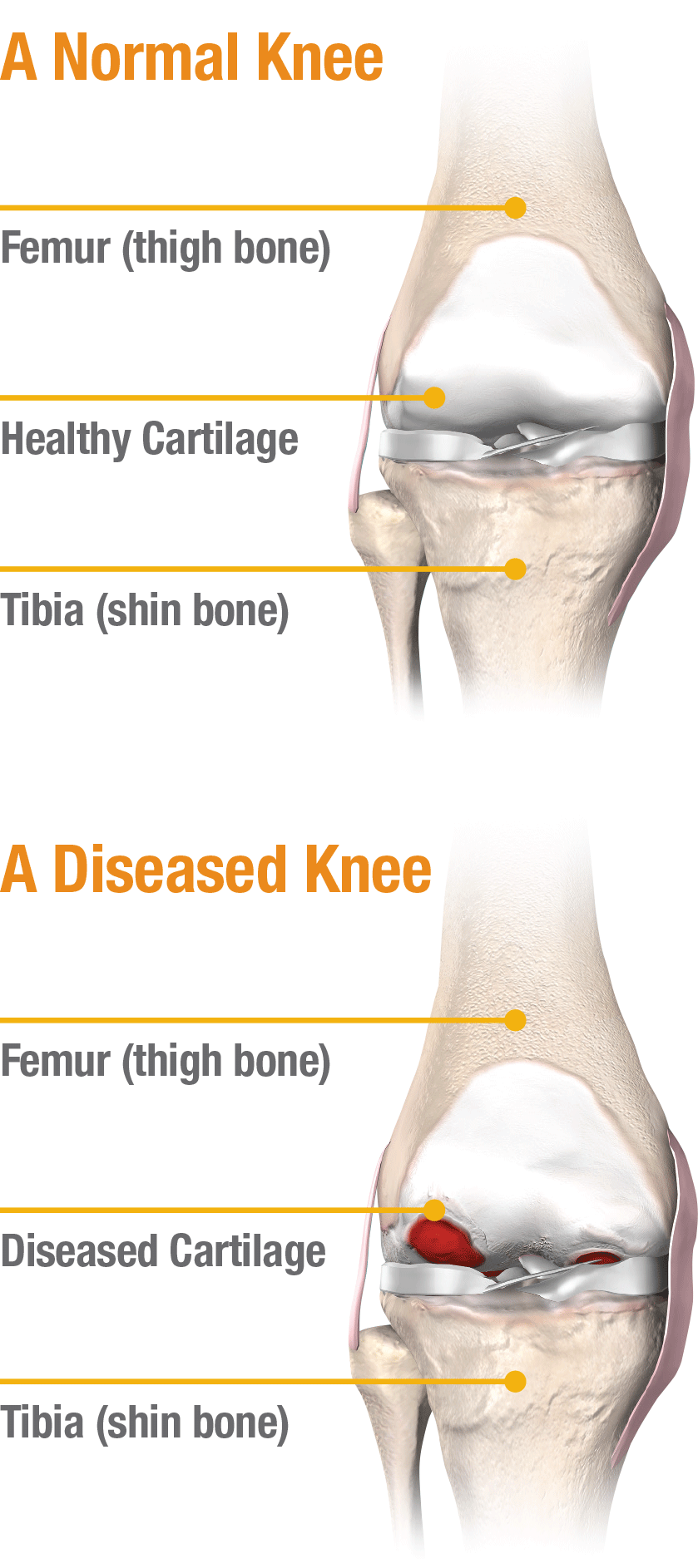
Knee joint replacement is intended for use in individuals with joint disease resulting from degenerative, rheumatoid and post-traumatic arthritis, and for moderate deformity of the knee. Joint replacement surgery is not appropriate for patients with certain types of infections, any mental or neuromuscular disorder which would create an unacceptable risk of prosthesis instability, prosthesis fixation failure or complications in postoperative care, compromised bone stock, skeletal immaturity, severe instability of the joint, or excessive body weight.
Like any surgery, joint replacement surgery has serious risks which include, but are not limited to, pain, bone fracture, change in the treated leg length (hip), joint stiffness, hip joint fusion, amputation, peripheral neuropathies (nerve damage), circulatory compromise (including deep vein thrombosis (blood clots in the legs)), genitourinary disorders (including kidney failure), gastrointestinal disorders (including paralytic ileus (loss of intestinal digestive movement)), vascular disorders (including thrombus (blood clots), blood loss, or changes in blood pressure or heart rhythm), bronchopulmonary disorders (including emboli, stroke or pneumonia), heart attack, and death.
Implant related risks which may lead to a revision of the implant include dislocation, loosening, fracture, nerve damage, heterotopic bone formation (abnormal bone growth in tissue), wear of the implant, metal sensitivity, soft tissue imbalance, osteolysis (localized progressive bone loss), audible sounds during motion, and reaction to particle debris.
The information presented is for educational purposes only. Speak to your doctor to which therapy is appropriate for you. Individual results vary and not all patients will return to the same activity level. The lifetime of any joint replacement is limited and depends on several factors like patient weight and activity level. Your doctor will counsel you about strategies to potentially prolong the lifetime of the device, including avoiding high-impact activities, such as running, as well as maintaining a healthy weight. It is important to closely follow your physician’s instructions regarding post-surgery activity, treatment and follow-up care.
Speak to your doctor to decide which therapy/treatment is appropriate for you.
Stryker Corporation or its other divisions or other corporate affiliated entities own, use or have applied for the following trademarks or service marks: Mako, Stryker, Together with our customers, we are driven to make healthcare better. All other trademarks are trademarks of their respective owners or holders.
GSNPS-PE-85_17642